ArrayList介绍
以下是ArrayList源码的介绍:
1 | /** |
ArrayList的继承与接口实现:
1 | public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> |
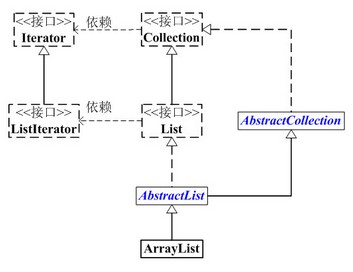
ArrayList继承了AbstractList,实现了List。它提供了相关的增加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandomAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能被克隆。
ArrayList实现java.io.Serializable接口,即ArrayList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
ArrayList与Collection关系如下:
ArrayList的构造器
ArrayList提供了三个构造器:
1.public ArrayList(int initialCapacity);
用指定的大小来初始化内部的数组
源码如下:
1 | /** |
2.public ArrayList();
默认的构造器,以默认大小(10)来初始化内部的数组。
源码如下:
1 | /** |
3.public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c);
用一个Collection对象来构造,并将集合的元素添加到ArrayList。
源码如下:
1 | /** |
ArrayList的常用方法:
1.添加方法:
(1) public boolean add(E e)
Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
(2) public void add(int index, E element)
Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this ist.
(3) public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E>c)
Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list,, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s Iterator.
(4) public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
list, starting at the specified position.
2.删除方法
(1) public E remove(int index)
Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
(2) public boolean remove(Object o)
Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,if it is present.
(3) private void fastRemove(int index)
Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not return the value removed.
(4) protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
(5) public void clear()
Removes all of the elements from this list.
(6) public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection.
3.修改方法
public E set(int index, E element)
Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element.
4.获取元素
public E get(int index)
Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
5.toArray()
(1) public Object[] toArray()
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence (from first to last element).
(按适当顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组。)
(2) public
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array.
(返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。)
6.trimToSize
public void trimToSize()
Trims the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be the list’s current size.
这个方法用于将ArrayList固定到实际元素的大小,当动态数组元素确定不再添加的时候,可以调用这个方法来释放空余的内存。
7.其他
(1) public int indexOf(Object o)
Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
(2) public int lastIndexOf(Object o)
Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
(3) public boolean contains(Object o)
(4) public boolean isEmpty()
(5)public int size()
ArrayList的遍历方式及效率比较
遍历ArrayList的方法有如下几种:
1.Iterator迭代器方式遍历
(1)Iterator的while实现
1 | Iterator<Integer> iter=list.iterator(); |
(2)Iterator的for实现
1 | for (Iterator<Integer> iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) { |
2.随机访问,通过索引值去遍历get(index)
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
1 | //基本的for |
3.单用foreach语句遍历
1 | for (Integer value : list) { |
遍历方式间的比较
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess随机访问接口,因此它对随机访问的速度快,而基本的for循环中的get()方法,采用的即是随机访问的方法,因而在ArrayList中,for循环速度快。
LinkedList采取的是顺序访问方式,iterator中的next()方法,采用的即是顺序访问方法,因此在LinkedList中,使用iterator的速度较快。
for、foreach、iterator的区别:
(1)条件上:
for需要知道集合或数组的大小,还要是有序的,否则无法遍历。
foreach和iterator不需要知道集合或数组大小,他们是得到集合内的每个元素后进行处理。
(2)多态上:
for和foreach都需要先知道集合的类型,甚至是集合内元素的类型,不能实现多态。
iterator是个接口类型,不需要关心所遍历的序列的类型,能够将遍历序列的操作与序列底层的结构分离。迭代器统一了对容器的访问方式。
(3)用法上:
for循环一般用来处理比较简单的有序的,可预知大小的集合或数组。
foreach可用于遍历任何集合或数组,但是需要知道集合内部类型。
iterator不需要知道元素和集合的类型,可以随时修改或者删除集合内部的元素。当需要对不同的容器实现同样的遍历方式时,可用迭代器。
总结起来,就是for需要知道大小;foreach需要知道类型;iterator既不需要知道大小,也不需要知道类型。